What is a Large Language Model (LLM)
18 Sep, 2025
Large Language Models (LLMs) are advanced AI systems built on deep neural networks designed to process, understand and generate human-like text. By using massive datasets and billions of parameters, LLMs have transformed the way humans interact with technology. It learns patterns, grammar and context from text and can answer questions, write content, translate languages and many more. Mordern LLMs include ChatGPT (OpenAI), Google Gemini, Anthropic Claude, etc
To explore the technical concepts behind LLMs, understand how they work, what they can do and how to build projects using them, refer to our Large Language Model (LLM) Tutorial.
Working of LLM
LLMs are primarily based on the Transformer architecture which enables them to learn long-range dependencies and contextual meaning in text. At a high level, they work through:
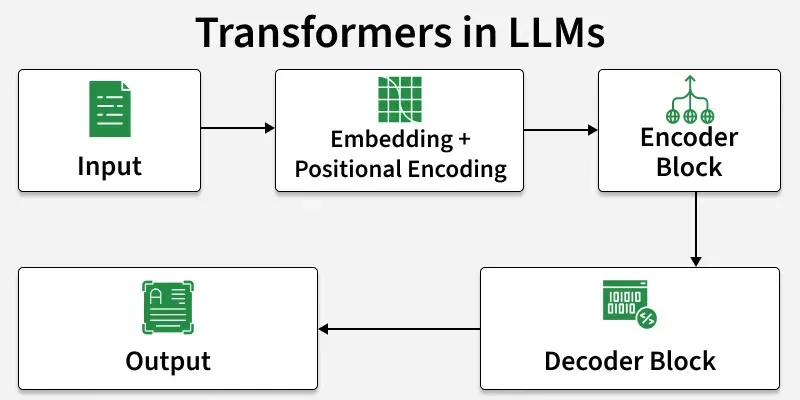
- Input Embeddings: Converting text into numerical vectors.
- Positional Encoding: Adding sequence/order information.
- Self-Attention: Understanding relationships between words in context.
- Feed-Forward Layers: Capturing complex patterns.
- Decoding: Generating responses step-by-step.
- Multi-Head Attention: Parallel reasoning over multiple relationships.
To know more about transformers architecture refer to: Architecture and Working of Transformers in Deep Learning
Architecture
The architecture of LLMs consist of multiple stacked layers that process text in parallel. Core components include:
- Embedding Layer: Converts tokens i.e words/subwords into dense vectors.
- Attention Mechanism: Learns context by focusing on relevant words.
- Feed-Forward Layers: Capture non-linear patterns and relationships.
- Normalization and Residual Connections: Improve training stability.
- Output Layer: Generates predictions such as the next word or sentence.
To know more about the architecture of LLM, read LLM Architecture.
Popular LLMs
Some of the most widely used LLMs include:
- GPT-4 and GPT-4o (OpenAI): Advanced multimodal reasoning and dialogue capabilities.
- Gemini 1.5 (Google DeepMind): Long-context reasoning, capable of handling 1M+ tokens.
- Claude 3 (Anthropic): Safety-focused, strong at reasoning and summarization.
- LLaMA 3 (Meta): Open-weight model, popular in research and startups.
- Mistral 7B / Mixtral (Mistral AI): Efficient open-source alternatives for developers.
- BERT and RoBERTa (Google/Facebook): Strong embedding models for NLP tasks.
- mBERT and XLM-R: Early multilingual LLMs.
- BLOOM: Large open-source multilingual model, collaboratively developed.
Use Cases
- Code Generation: LLMs can generate accurate code based on user instructions for specific tasks.
- Debugging and Documentation: They assist in identifying code errors, suggesting fixes and even automating project documentation.
- Question Answering: Users can ask both casual and complex questions, receiving detailed, context-aware responses.
- Language Translation and Correction: LLMs can translate text between over 50 languages and correct grammatical errors.
- Prompt-Based Versatility: By crafting creative prompts, users can unlock endless possibilities, as LLMs excel in one-shot and zero-shot learning scenarios.
Advantages
Large Language Models (LLMs) come with several advantages that contribute to their widespread adoption and success in various applications:
- Zero-Shot and Few-Shot Learning: Can perform new tasks without explicit retraining.
- Scalable Knowledge: Efficiently process and understand vast text corpora.
- Fine-Tuning Flexibility: Adaptable to specific industries and datasets.
- Automation of Language Tasks: Frees human effort from repetitive or time-consuming tasks.
- Versatility: Effective across multiple domains—healthcare, education, business and research.
Challenges
- High Costs: Training requires millions of dollars in compute resources.
- Time-Intensive: Training large models can take weeks or months.
- Data Challenges: Limited availability of high-quality, legal and unbiased text data.
- Environmental Impact: High energy consumption leading to significant carbon footprint.
- Ethical Concerns: Bias, misinformation risks and responsible deployment remains a major issue.
4 Questions
Which of the following historical developments significantly contributed to the advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs)?
-
A
Invention of the internet
-
B
Introduction of the Turing Test
-
C
Rise of deep learning algorithms
-
D
Development of quantum computing
What is the main objective of pre-training in large language models?
-
A
To fine-tune the model on specific tasks
-
B
To train the model on a large, labeled dataset
-
C
To give the model a broad foundational understanding of language
-
D
To evaluate the model’s performance on various tasks
Pre training exposes the model to large scale text data to learn general language patterns before fine-tuning.
What is a key reason for using Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods in Large Language Models?
-
A
They improve model accuracy by increasing the number of parameters
-
B
They reduce computational and memory costs while achieving performance close to full fine-tuning
-
C
They require training the entire model on every new dataset
-
D
They eliminate the need for pre-training altogether
PEFT allows fine-tuning large models efficiently, without retraining the entire network, saving compute and memory.
What is a key characteristic of a Large Language Model (LLM)?
-
A
It processes images and text simultaneously.
-
B
It is trained using millions or billions of parameters.
-
C
It only handles text data.
-
D
It requires minimal training data to work effectively.

1/4
1/4